What Is Attribution Modeling? A Complete Guide to Boost Your Marketing
So, what exactly is attribution modeling?
Think of it as the instant replay for your marketing. It’s the process of figuring out which marketing touchpoints—like that social media ad, a blog post they read, or an email you sent—actually get credit for a sale. It helps you stop guessing and start making decisions backed by real data.
Why Attribution Modeling Is Critical for Marketers
Imagine a customer’s path to buying from you is like a soccer game. The final purchase is the goal.
Along the way, multiple players (your marketing channels) pass the ball to each other before the final shot. Without attribution modeling, you’d only give credit to the player who scored the goal. You'd completely ignore the midfielders and defenders who made crucial assists to get the ball down the field. That kind of limited view leads to bad budget decisions and a lot of missed opportunities.
This is the exact problem attribution modeling solves. It gives you a clear framework to see how different channels work together to influence a customer's final decision. By looking at the entire journey, you can pinpoint which efforts sparked the initial interest, which ones kept them engaged, and which one finally sealed the deal.
This infographic paints a great picture of the customer journey, showing it as a series of connected plays leading up to a goal.
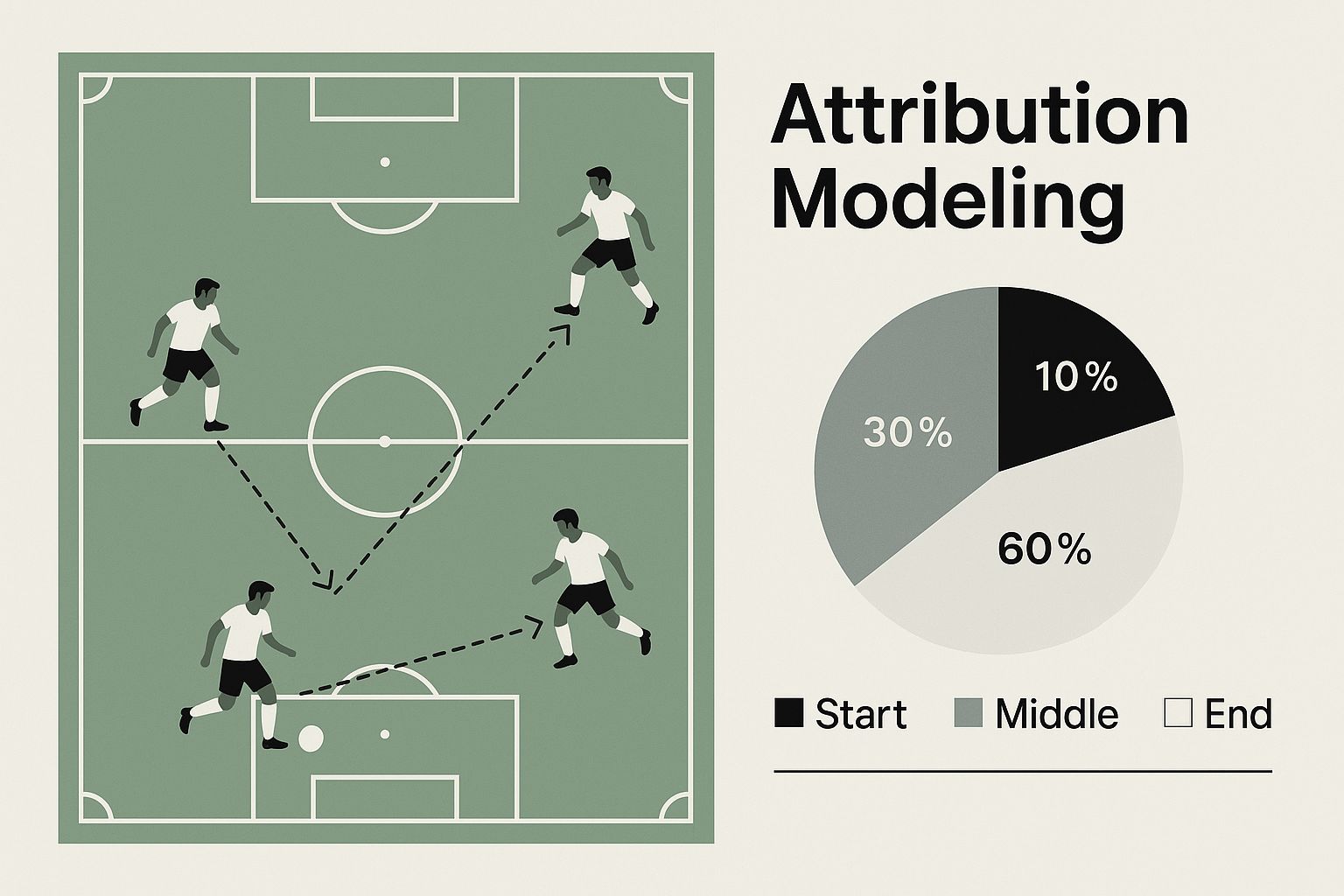
It’s a powerful reminder that conversions are almost never the result of a single action. They come from a sequence of well-coordinated marketing efforts.
From Confusion to Clarity
Attribution modeling was born from one of marketing’s oldest headaches: figuring out which actions actually bring in the money.
Historically, it was a mess. It wasn't uncommon for multiple campaigns to claim credit for the very same sale. For example, back in the early 2000s, one U.S. bank found that an average sales dollar was being attributed to seven different marketing campaigns because of all the overlapping touchpoints.
Modern attribution is all about untangling that web to give you clear insights that sharpen your entire strategy.
Attribution modeling isn't just about giving credit where it's due; it's about understanding the synergy between your marketing channels to build a more effective, efficient, and predictable growth engine.
When you put a solid attribution model in place, you unlock some serious advantages:
- Smarter Budget Allocation: You can confidently move your money to the channels that are actually delivering the highest return on investment (ROI).
- Improved Campaign Performance: Once you know which touchpoints are working best, you can fine-tune your messaging and creatives for even better results.
- Demonstrated Marketing Value: You finally have the proof you need to show stakeholders exactly how marketing is driving revenue.
At its core, attribution modeling relies on rock-solid conversion tracking to collect all the data points along the customer journey. To get a better handle on the big picture, check out this complete guide to marketing attribution. And if you're just starting out, our guide on what is conversion tracking is the perfect place to build your foundation.
The Different Flavors of Attribution Modeling

Alright, you get why attribution is a big deal. Now for the fun part: figuring out how to actually assign that credit. Think of each attribution model as a different lens for viewing your customer’s journey. The one you choose can completely change your understanding of which channels are pulling their weight and which are just along for the ride.
Models generally fall into two big buckets: single-touch and multi-touch.
Single-touch models are the simplest of the bunch. They give 100% of the credit for a conversion to just one interaction. It's a blunt instrument, for sure, but sometimes that's all you need.
Multi-touch models, on the other hand, are built on the reality that most purchases don't happen after a single click. They spread the credit across several touchpoints, giving you a much more balanced picture of your marketing performance.
Single-Touch Attribution Models
Single-touch models are incredibly straightforward and a common starting point for businesses just dipping their toes into attribution. They focus on one make-or-break moment: the very beginning or the very end of the journey.
First-Touch Attribution
This one is simple: 100% of the credit goes to the very first interaction someone has with your brand. Let's say a user discovers your company by reading a blog post. Weeks later, they see a Facebook ad, click it, and finally make a purchase. With this model, that initial blog post gets all the glory.
- Best For: Companies laser-focused on top-of-funnel marketing and figuring out how people discover them in the first place.
- Key Question It Answers: "Where are new customers first hearing about us?"
Last-Touch Attribution
You can probably guess this one. It's the polar opposite, giving 100% of the credit to the final interaction before a conversion. In our example above, the Facebook ad—the last thing they clicked before buying—would get all the credit. The blog post gets nothing.
- Best For: Businesses with short sales cycles who want to know what's sealing the deal.
- Key Question It Answers: "What's the final nudge that gets people to convert?"
Both of these models are a bit like giving all the credit for a Super Bowl win to either the quarterback who made the first pass or the kicker who scored the final field goal. They're telling part of the story, but they're ignoring the entire game played in between.
Multi-Touch Attribution Models
If you want the whole story, you need to look at multi-touch attribution. These models operate on a simple truth: the "messy middle" of the customer journey matters. A lot. They distribute credit across multiple touchpoints, painting a far more realistic picture of how all your marketing efforts work together.
Linear Model
The Linear model is the most democratic of the bunch. It splits the credit equally across every single touchpoint on the path to conversion. If a customer saw a social post, opened an email, clicked a paid ad, and then visited your site directly before buying, each of those four touchpoints would get a clean 25% of the credit.
- Best For: Marketers who value every interaction and want a high-level view of the entire customer path.
- Key Question It Answers: "Which channels consistently show up in our conversion journeys?"
Time-Decay Model
The Time-Decay model works on the assumption that the closer a touchpoint is to the sale, the more influence it had. An ad someone saw yesterday is probably more important than one they saw three weeks ago. So, it gives more credit to the interactions that happen closer to the conversion.
This is a smart way to think about complex customer journeys. Nielsen data shows that over 50% of customer paths involve more than one interaction, so weighting them makes sense. You might see a model where an early touchpoint gets 10%, while the final one gets 40%. For a deeper dive into consumer interaction data, you can review attribution insights from Aerospike.
- Best For: Companies with longer sales cycles, like in B2B, where nurturing over time is crucial.
- Key Question It Answers: "Which recent touchpoints are accelerating our deals?"
The Time-Decay model is built on a simple premise: a marketing touchpoint's influence fades over time. An ad seen yesterday is likely more impactful than one seen a month ago.
U-Shaped (Position-Based) Model
The U-Shaped model spotlights two pivotal moments: the first touch (the introduction) and the lead-creation touch (the moment they officially became a lead, like filling out a form). It typically gives 40% of the credit to each of these bookend events, then sprinkles the remaining 20% evenly across all the interactions in the middle.
- Best For: Businesses focused on lead generation, where both finding new prospects and converting them into leads are mission-critical.
- Key Question It Answers: "What's best at generating awareness, and what's best at creating qualified leads?"
W-Shaped Model
Taking the U-Shaped model a step further, the W-Shaped model adds a third major milestone: the opportunity-creation touch (when a lead becomes a sales opportunity, like booking a demo).
In this setup, the first touch, lead-creation touch, and opportunity-creation touch each get 30% of the credit (totaling 90%). The last 10% is divided among the remaining touchpoints. This model is perfect for businesses with a defined sales pipeline where these three moments are the most important steps toward a final sale.
- Best For: Companies with longer, more complex sales funnels that have clear marketing-to-sales handoff points.
- Key Question It Answers: "Which efforts are driving awareness, creating leads, and generating real sales opportunities?"
At a Glance: Comparing The Models
To make it easier to see how these rule-based models stack up, here’s a quick comparison table that breaks down how each one assigns credit and what it’s best used for.
| Model Type | How It Assigns Credit | Best For Measuring |
|---|---|---|
| First-Touch | 100% credit to the first interaction. | Top-of-funnel brand awareness. |
| Last-Touch | 100% credit to the final interaction before conversion. | Bottom-of-funnel conversion channels. |
| Linear | Credit is split equally among all touchpoints. | The overall impact of the full customer journey. |
| Time-Decay | More credit to touchpoints closer to the conversion. | Channels that accelerate sales in long cycles. |
| U-Shaped | 40% to first touch, 40% to lead creation, 20% to middle. | Lead generation and initial discovery. |
| W-Shaped | 30% each to first touch, lead creation, & opportunity creation. | The full funnel from awareness to sales opp. |
Choosing the right model is less about finding a single "correct" answer and more about picking the one that tells the most useful story for your business goals. Each one reveals a different truth about what's really driving your growth.
The Power Of Data-Driven Attribution
While rule-based models give you a straightforward, logical way to assign credit, they’re ultimately built on assumptions. Models like Linear, Time-Decay, or W-Shaped are solid starting points, but they apply the same rigid rules to every single business, no matter how unique their customer journeys are. This is where the next evolution in marketing measurement comes into play: data-driven attribution.
Instead of forcing your data into a pre-built template, data-driven attribution uses machine learning to analyze your specific conversion history. It looks at every touchpoint across thousands of customer paths—both the ones that converted and the ones that didn't—to figure out the actual statistical impact each interaction had. In other words, it learns from your business's unique performance patterns.
Think of it like this: rule-based models are like using a generic city map. A data-driven model is like having a real-time GPS that knows your exact starting point, your destination, and all the current traffic, rerouting you for the best path. It's customized just for you.
How Algorithmic Models Work
At its core, a data-driven model figures out a probability baseline. It studies the sequences of touchpoints that led to sales and compares them to the paths that went nowhere. By spotting which channels pop up more often in successful journeys, the algorithm assigns credit based on their proven influence.
This approach finally opens up the "black box" of customer behavior, revealing insights that fixed models almost always miss. For example, it might discover that a specific blog post, while rarely the last click, is a powerhouse for introducing high-value customers who convert weeks later. A last-touch model would give it zero credit, but a data-driven model sees its true contribution.
By 2023-2025, the marketing world has leaned heavily into these algorithmic techniques. While old-school models use fixed rules that often oversimplify things, data-driven models chew through massive historical datasets—including clicks and engagement metrics—to calculate the true weight of each touchpoint. Google's data-driven attribution in GA4, for instance, uses concepts from cooperative game theory (like the Shapley value) to fairly distribute credit. You can find more insights about these advanced attribution models on OWOX.com.
Key Advantages Of A Data-Driven Approach
Switching to an algorithmic model brings some serious benefits that can sharpen your entire marketing strategy. When you let the data tell the story, measuring marketing campaign effectiveness becomes far more accurate.
Here are the main advantages:
- Uncover Hidden Influencers: It's brilliant at identifying the true value of top- and mid-funnel channels that assist conversions without ever being the final click.
- Adapts to Your Business: The model isn’t static. It learns and evolves right along with your marketing performance and customer behavior.
- Objective Credit Assignment: It removes guesswork and bias from the equation, assigning credit based on cold, hard data instead of human assumptions.
A data-driven model’s greatest strength is its ability to learn. It doesn’t just tell you what happened; it quantifies the contribution of each step, giving you a much more accurate foundation for future budget decisions.
What You Need To Get Started
There's one catch to this advanced approach, and it's a big one: data volume. For the machine learning algorithms to do their job properly, they need a ton of conversions and touchpoints to analyze.
Platforms like Google Analytics 4 require a minimum of 300 conversions and 10,000 user paths within a 30-day period just to turn on their data-driven model. If your numbers are below that threshold, the model won't have enough information to work with, and you're probably better off sticking with a rule-based model for now. This ensures you're building insights on a solid foundation, which is crucial for accurate customer acquisition cost calculation and improving your marketing ROI.
How To Choose The Right Attribution Model
Picking the right attribution model isn't about finding some mythical "best" option. It’s about finding the model that mirrors your business reality. The one that works wonders for a fast-fashion eCommerce brand could be completely misleading for a B2B software company.
Getting this right means taking a hard look at your goals, your sales cycle, and just how many channels you're juggling.
Think of it like picking a tool from a toolbox. You wouldn't use a sledgehammer to hang a picture frame. In the same way, applying a Last-Touch model to a six-month sales journey is just asking to be misled. You'll end up confused about your marketing performance and, worse, throwing money down the drain.
To nail this, you need to answer three core questions. Your answers will point you straight to the model that gives you the most clarity.
What Is Your Primary Business Goal?
First up, what are you actually trying to do? Your main objective is the most important piece of the puzzle. Are you trying to get your name out there, or are you focused on closing deals?
-
Goal: Brand Awareness. If your top priority is introducing your brand to new people, then First-Touch is your best friend. It’s brilliant at showing you which channels are bringing fresh faces into your world.
-
Goal: Direct Sales. On the flip side, if you're all about converting known leads and driving revenue, a Last-Touch model is way more useful. It shines a spotlight on those final, bottom-of-the-funnel actions that nudge people over the finish line.
-
Goal: Lead Nurturing. For most businesses, it's not that simple. You need to generate leads and warm them up over time. In that case, a U-Shaped or W-Shaped model gives you a more balanced picture. These models credit the big milestones—first touch, lead creation, and final sale—reflecting a more realistic funnel.
How Long Is Your Sales Cycle?
Next, think about how long it takes for a customer to go from "hello" to "here's my credit card." The length of your sales cycle completely changes which models will give you an honest view.
A flash sale for an online store might have a sales cycle that lasts a few hours, maybe a day. In that situation, a Last-Touch model is often a perfect fit. Why? Because that final ad or email really was the most influential touchpoint. It reflects the impulsive, quick decision.
But what about a B2B SaaS company with a six-month sales cycle? You've got demos, proposals, and multiple decision-makers involved. Here, a Last-Touch model is practically useless. It completely ignores the months of blog posts, webinars, and emails that built the relationship.
For those longer journeys, models like Time-Decay or Linear are far more powerful because they actually acknowledge and value all those earlier interactions.
Choosing a model that doesn't match your sales cycle is like trying to read only the last page of a book and expecting to understand the entire plot. You miss all the crucial character development that happened along the way.
How Complex Is Your Channel Mix?
Finally, how many different marketing channels are you using? The more complex your strategy, the more sophisticated your attribution model needs to be.
If you’re only running a couple of channels, like Google Ads and an email list, a simple model might be all you need. Single-touch models can give you clear data when the customer journey itself is straightforward.
But if you’re juggling social media, content marketing, paid search, affiliates, and events, the customer's path is anything but simple. A multi-touch model isn't a nice-to-have; it's a must.
- A Linear model is a great starting point, giving every channel an equal slice of the pie.
- Time-Decay is perfect for understanding which channels are best at accelerating deals toward a close.
- A Data-Driven model is the holy grail for complex marketing. It uses your own performance data to assign credit objectively, revealing the true influence of each touchpoint without any guesswork.
Implementing Your Attribution Strategy

Okay, so you understand the theory. Now for the fun part: putting it all into practice. This is where the real value gets unlocked, but it's not as simple as flipping a switch. Think of it less like a quick fix and more like building a solid foundation, brick by brick, with clean data and clear goals.
The absolute first step? Getting your cross-channel tracking consistent. This is the bedrock of your entire strategy. If you don't have reliable data flowing from every single customer touchpoint, your models will be built on quicksand. The insights you get will be misleading at best, and flat-out wrong at worst.
This is where tools like UTM parameters become your best friend—they're non-negotiable. UTMs act like digital breadcrumbs, letting your analytics platform trace a user's journey across every campaign, source, and ad. When you use them consistently, you know exactly where someone came from, whether it was a specific Facebook ad or your Tuesday morning email newsletter.
Laying The Groundwork For Success
Before you even dream about picking a model, you have to get your data house in order. This means making sure your key platforms, like your CRM and analytics tools, are actually talking to each other. When these systems are integrated, you finally get that unified, single view of the customer journey, from the first ad they saw to the moment they hit "buy."
A huge piece of this groundwork is data hygiene. Let's be honest, dirty, inconsistent, or incomplete data will completely sabotage your efforts. You have to take the time to clean up your records, standardize how you name your campaigns, and double-check that all your tracking codes are firing correctly.
To keep everything in one place, it’s worth learning how to build a robust marketing campaign tracking spreadsheet. It can serve as your single source of truth and keep your team aligned.
Your Step-By-Step Implementation Plan
Once your data foundation is solid, you can move forward with a clear plan. Following these steps will help you roll out your attribution efforts with confidence.
-
Define Clear Conversion Goals: What action actually means "success" for your business? Is it a completed purchase? A demo request? A simple form submission? Get specific, because this is the exact event your model will be built around.
-
Select a Baseline Model: Don't chase perfection from day one. Start simple. Pick a basic, rule-based model like Last-Touch or Linear. This gives you an immediate baseline you can use to start gathering insights and compare against more sophisticated models down the road.
-
Analyze and Iterate: Your first model is a starting point, not the finish line. Constantly review the insights it’s giving you. Does it make sense with what you’re seeing in the market? Are there obvious blind spots? Use what you learn to test different models until you find one that truly reflects how your business grows.
The goal of implementation isn't to find the one "perfect" attribution model. It's to build a system of continuous measurement and improvement, where each iteration brings you closer to understanding the true drivers of your growth.
A common pitfall to avoid is siloed data. If your social media, email, and sales data all live in separate, disconnected worlds, you’ll never see the full customer journey. Integrating these sources is absolutely essential. And don't forget about offline touchpoints like events or direct mail if they're a big part of your strategy—find a way to get that data into your system, too.
The Future Of Marketing Attribution
So we’ve covered a lot of ground on attribution models. They're an awesome lens for seeing what’s working. But let’s be real—the ground is constantly shifting under our feet.
Modern marketing is messy. The idea of getting a perfect, crystal-clear map of every single customer journey is getting tougher by the day. As marketers, we're all wrestling with some major challenges that are forcing the entire game to change.
One of the biggest headaches is cross-device tracking. Think about your own behavior. You might see an ad on your work laptop, do some research on your tablet at home, and finally pull the trigger and buy on your phone. Trying to stitch that fragmented journey together into one coherent story? That’s a massive technical lift.
Navigating A Privacy-First World
Now, throw in the massive shifts happening in user privacy. We’re all talking about it. The phase-out of third-party cookies and tougher rules like GDPR are completely rewriting the rulebook on how we track user behavior.
This "cookiepocalypse" basically means the old-school ways of following users across different websites are dying off. That leaves some serious blind spots in our attribution data, and relying on those fading methods just isn't a sustainable strategy anymore.
The future of attribution isn't about finding a clever workaround for privacy rules. It's about building a smarter, more resilient measurement system that respects user consent while still giving us the insights we need to grow the business.
The Rise Of Unified Measurement
So, what's next? The most promising path forward is what the industry is calling unified measurement frameworks. Instead of leaning on just one attribution model and hoping for the best, this approach blends different methods to paint a much more complete and accurate picture.
This usually means combining two powerful techniques:
- Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM): This is a "top-down" way of looking at things. It uses statistical analysis to see how high-level stuff—like total ad spend, seasonality, or even economic trends—impacts sales over time. It's fantastic for getting the big picture and measuring offline channels like TV and radio ads.
- Digital Attribution: This is the "bottom-up" approach we've been talking about, zeroing in on individual user touchpoints across all our digital channels.
By blending the macro-level view from MMM with the nitty-gritty details of digital attribution, we can finally get a holistic view that covers everything, online and off. It helps us overcome the blind spots that each method has on its own.
The Growing Role Of Artificial Intelligence
Looking even further down the road, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is about to play a much bigger part. Predictive modeling, supercharged by machine learning, is going to take us way beyond just giving credit for stuff that already happened. It’s going to start forecasting the likely impact of our future marketing decisions.
Imagine having a system that could tell you the probable ROI of shifting 15% of your budget from paid search over to connected TV—before you spend a single dollar. That's the promise of AI-driven attribution. It's about turning measurement from a reactive, look-in-the-rearview-mirror exercise into a proactive, strategic weapon.
Even with all the new challenges popping up, this evolution ensures we can keep doing what matters most: proving marketing's value.
A Few Common Questions About Attribution Modeling
As you start putting these ideas into practice, a few questions always seem to come up. Let's tackle them head-on to clear up any confusion and get you ready to roll.
Single-Touch Vs Multi-Touch Attribution
So, what's the real difference between single-touch and multi-touch attribution? It's kind of like comparing a single snapshot to a full-length movie.
Single-touch models like First-Touch or Last-Touch are the snapshot. They give 100% of the credit to one specific moment—either the very first time someone saw your brand or the very last click before they converted. They're simple and can be useful for narrow goals, like figuring out what's driving initial awareness.
Multi-touch models, on the other hand, show you the whole movie. Whether it's Linear, U-Shaped, or another variation, they spread the credit across multiple touchpoints. This approach recognizes that the middle of the journey is just as important, giving you a much more realistic picture of how all your marketing channels work together.
How Much Data Do I Need For Data-Driven Models?
This is a big one. How much data do you actually need to make a data-driven model work? The short answer: a lot.
These algorithmic models need a ton of data to learn your customers' unique buying patterns. For example, Google Analytics 4 won't even turn on its data-driven model until you have at least 300 conversions and 10,000 user paths in a 30-day period.
Without enough data, a data-driven model is just guessing. If you're not hitting those kinds of numbers, you're far better off sticking with a rule-based model. Otherwise, you risk making bad decisions based on shaky insights.
Can You Really Track Offline Marketing Channels?
Absolutely. But tracking things like TV ads, print, or trade shows requires a little creativity. You can't just slap a tracking pixel on a billboard, but you can definitely measure its impact.
Here are a few proven ways to do it:
- Unique Promo Codes: Create a specific discount code just for that TV ad or event.
- Dedicated URLs: Use a simple, memorable URL (like "yourbrand.com/radio") in your offline ads.
- "How Did You Hear About Us?" Surveys: Just ask! A simple question during checkout can provide incredibly valuable data.
By funneling these offline signals into your analytics, you can start building a truly complete picture of what's driving your growth.
Ready to stop wasting time on manual lead downloads and start converting customers faster? LeadSavvy Pro automates your Facebook lead capture, syncing new leads directly to your tools in real-time. Try LeadSavvy Pro for free and streamline your entire lead management process.







